Cold logistics. How to achieve an energy-efficient refrigerated warehouse (part I)

Most daily food products require refrigeration to guarantee their quality and avoid health problems.
Factors such as household consumption, exports and imports, and the increased online trade of fresh goods generate increased volumes of products requiring maintenance at a controlled temperature.
Logistics operations for refrigerated and frozen goods, such as in the food sector or pharmaceutical industry, require more demanding and rigorous processes than those not requiring controlled temperature storage. Given that incorrect handling in the logistics operation can interrupt the cold chain. In food products, cold chain interruption is easy to identify, as the product’s deterioration is visible. However, for pharmaceutical products, such as in the case of vaccines, this deterioration cannot be identified and the consequences of using them in poor condition are incalculable.
What is the cold chain?
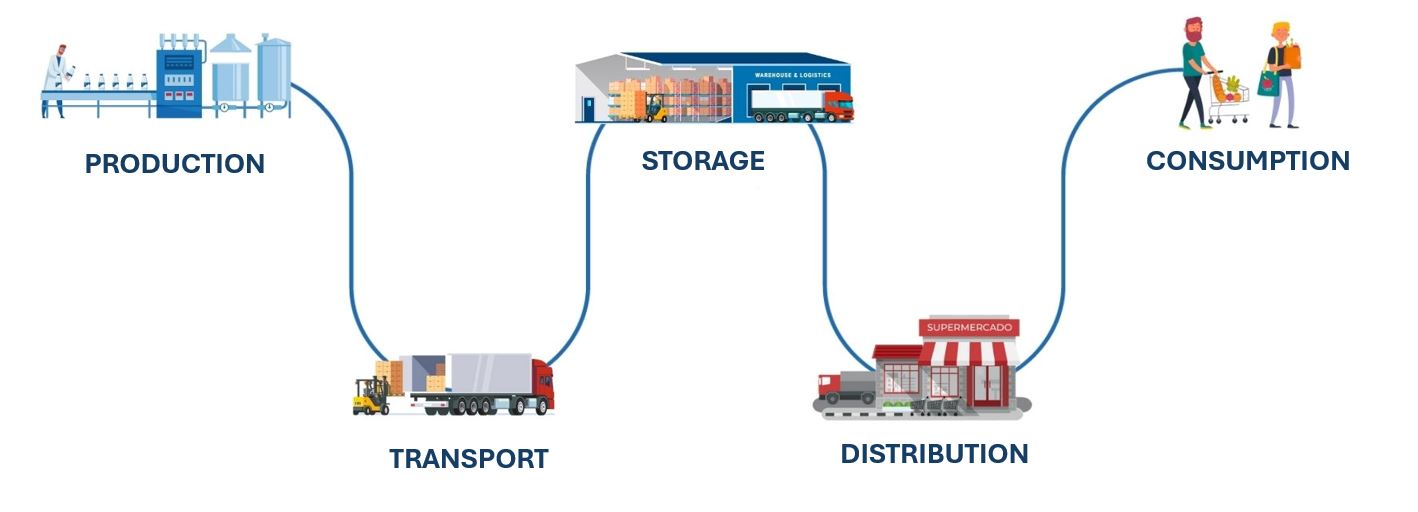
The cold chain comprises a series of production, storage and distribution activities for refrigerated goods that maintain the quality of these products by means of controlled temperature processes. This temperature must be stable and regular from harvesting or production until reaching the end consumer.
Most products need to be frozen or refrigerated within a temperature range: for frozen products temperatures must be below – 18 ºC and for refrigerated goods above 0ºC. At the same time, there is a maximum storage timeframe according to the type of product and storage environment.
Key points to be considered before designing a refrigerated storage facility:
In the design of refrigerated warehouses, we will pay special attention to the following aspects. Although also applicable to non-refrigerated goods warehouses, the importance is greater for these due to the energy cost involved to maintain this type of facility.
- Determining the installation’s requirements based on the type of load to be stored, given that it will have specific characteristics and handling needs.
- Knowing the volume of goods to be stored to scale the installations and cold stores.
- Homogenising the load and its reception adapting it to formats that facilitate access: pallets, crates, bags, etc.
- Establishing good flows in and out to determine service areas and cold store capacities.
- Being familiar with the seasonality of the goods to predict purchasing and dispatching peaks.
Refrigerated warehouse equipment:
Cold stores:
Store dimensions will be suitably designed for storage of the stock and possibility of preparing orders in them.
The technical-sanitary regulation of general conditions for refrigerated storage of food and food products lays down the following most frequent types of cold storage facility:
COMMON TYPES OF COLD STORE:
- ATMOSPHERE-CONTROLLED COLD STORE: For low rotation.
- MEDIUM AND HIGH ROTATION COLD STORE: Thermally insulated premises, inside which the required temperature and relative humidity can be kept constant through use of a refrigeration plant.
- FREEZER STORE: To receive previously frozen foods and food products.
- REFRIGERATED PRODUCT STORE: To receive and store previously refrigerated foods and food products.
- BI-TEMPERATURE STORE: To receive and store, alternatively, previously refrigerated or frozen foods and food products.
- MIXED STORE FOR COOLING AND REFRIGERATED PRESERVATION: To be able to cool products placed in the store at room temperature within a maximum of 24 hours, and then maintain them at the adequate refrigerated storage temperature.
- TUNNEL FREEZER: For quick freezing of foods.
Refrigerated stores will be installed on conventional flooring with a rough dustproof finish to avoid falling or tripping, in addition to insulating and thermal flooring with aeration to prevent the paving from freezing.
Racking systems for refrigerated warehouses:
How to choose the most appropriate racking system for your refrigerated warehouse
The storage system is an indispensable part of the logistics chain. Depending on the client’s needs we will choose one system or another, always bearing in mind that the racking system must:
- Optimise the space: we will choose a storage system that allows us to achieve the maximum possible storage capacity for the same surface. In this way, we will lower the cost of refrigeration.
- Racking used in cold installations is the same as in room-temperature installations, as they are suitable for any need and situation. However, if we need the shelves to withstand adverse conditions such as rust or corrosion, we can choose racks with a galvanised finish.
- Facilitate access to load units. By reducing transit in refrigerated zones, we will avoid the risk of condensation inside the stores.
- Avoid unnecessary movements of operators at low temperatures. Working at low temperatures lowers productivity and increases the risk of suffering accidents.
For cold storage we will choose systems that allow the load to be more compacted, in addition to automated or semi-automated systems to avoid exposure to low temperatures for the warehouse operators. In this post we explain the systems we recommend for cold storage.
Handling equipment:
We will choose handling equipment that is suited to our storage system. In the case of refrigerated warehouses, we must also choose equipment that is suitable for working in cold environments and at extreme temperatures.
If we do not choose equipment that is specific for refrigerated stores, cold can affect the battery, electrical components and bodywork of the handling equipment.
For this type of stores, there are also completely sealed and heated cabins for operators to keep warm inside them and achieve a higher productivity while working at low temperatures.
In warehouses at – 0ºC temperatures, it is not possible to work using handling equipment with diesel-fuel engines and batteries cannot be charged either in zones with below zero temperatures.
If we want to have the forklift charging point inside the refrigerated store zone, we will choose a forklift with lithium-ion batteries. In this way, we will be able to charge the forklift during resting periods, avoiding replacing batteries, and problems with condensation.
Another point in favour of lithium-ion batteries is that in cold environments they barely lose performance, are more energy-efficient, and last up to 3 times longer than a lead-acid battery.
IMPORTANT: The forklift battery.
Lithium-ion (LI-ION) batteries are the most ideal for cold environments as they barely lose performance at low temperatures, last three times as long, and are 30% more energy-efficient compared to lead-acid batteries.”
Environmental care and energy saving in cold storage
There is growing awareness of the importance of reducing energy consumption and corporate responsibility in caring for the environment .
Controlling these factors can help to reduce the energy consumption of your refrigerated warehouse:
- Correctly designing the layout of your refrigerated warehouse.
- Installing energy-saving devices: In standard freezer and refrigerated warehouses, the energy consumption is 3.5 and 4kWh/m3/month. However, those that incorporate energy-saving devices, have consumption levels of between 2.7 and 3kWh/m3/month. This translates into an energy saving of more than 20%.
- Paying attention to air distribution inside the building.
- Ensuring good insulation, especially in walls, floors, ceilings, and doors, to avoid temperatures gains or losses.
- Installing electronic operating controls.
- Using ammonia as a refrigerant reduces energy consumption and has no greater environmental impact than other refrigerants. The trend in future will be to use CO2, considered to be a green refrigerant.
There is growing awareness of the importance of reducing energy consumption and corporate responsibility in caring for the environment . For this reason, it is common for state-of-the-art warehouses to already incorporate energy-saving and environmental protection devices. In standard freezer and refrigerated warehouses, energy consumption is usually 3.5 and 4kWh/m3/month. However, those that incorporate energy-saving devices, have consumption levels of between 2.7 and 3kWh/m3/month. This translates into an energy saving of more than 20%.
To find out more about warehouse design, in this post we explain the factors to bear in mind and main zones to consider in your warehouse layout.
Choosing an expert supplier in refrigerated installations is extremely important.
The installation’s design must take into account customer requirements, considering the initial investment outlay, achievable energy cost reduction, and the energy saving to be made throughout the useful life of the refrigerated store. As cost-saving and energy-consumption are of the utmost importance in the cold sector.
Tailor-made solution
If you are not sure which storage solution best suits your needs, please contact us. We will help you get your project off the ground.


